The first birth of Three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment unit is in the US auto market. To comply with stricter emissions regulations from the United States Environmental Protection Agency. Most gasoline-powered vehicles starting in 1975 must be equipped with a three-way catalytic exhaust aftertreatment unit. And today it has become very popular on road vehicles.
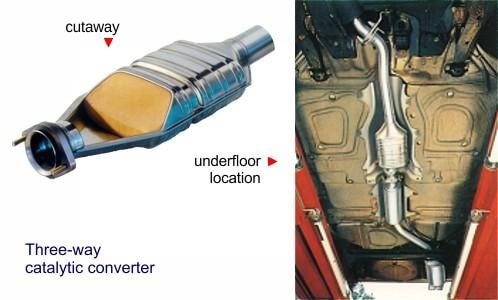
Three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment unit
What is a three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment unit?
3-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment is one device that converts harmful gases and pollutants in exhaust gases from internal combustion engines into less toxic substances by a catalytic redox process (an oxidation and reduction process). Three-way catalytic converters are commonly used with internal combustion engines. The fuel used is gasoline or diesel
Why should we use three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment?
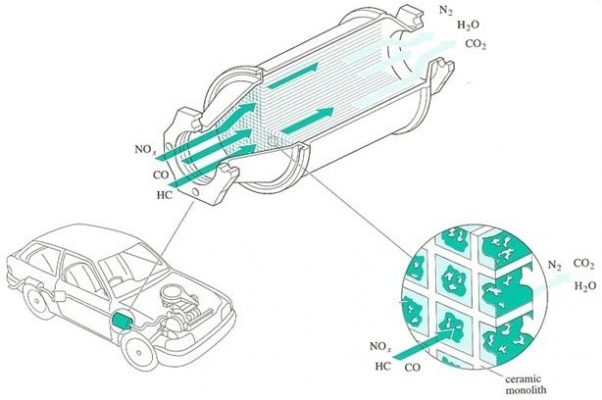
Engine exhaust contains harmful substances such as nitrogen oxide (NOx), carbonmonoxide (CO) and Hydrocarbon (HC). These substances seriously affect human health and the environment. 3-way catalytic exhaust gas processor converts this harmful substance into less harmful nitrogen (N2), carbondioxide (CO 2) and water.
Mechanism of action
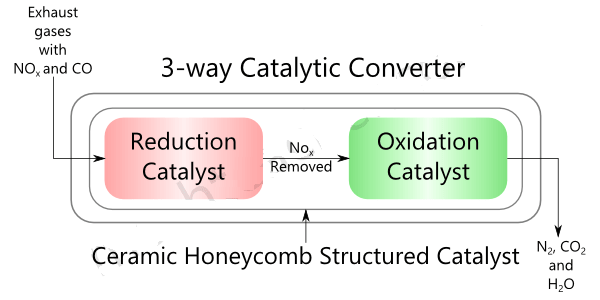
A 3-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment unit used two catalysts to convert harmful gases into less toxic gases. The catalyst for the reduction process is made from Rodium (Rh). While the catalyst for oxidation is made from platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd). Both catalysts are directly impregnated on the surface of the honeycomb ceramic core. This ceramic core is coated on the outer surface with aluminum oxide. They have good wear and friction resistance after heat treatment at a temperature of about 10000C
The operating mechanism of the 3-way catalytic exhaust gas processor
Three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment stages
Phase 1 – NOx reduction process
First, the exhaust gas is passed through a Rodi (Rh) catalyst. It converts nitrous oxide (NOx) into nitrogen (N 2) and oxygen (O2). The following reactions take place when the exhaust gas passes through a reduction catalyst.
2NO → N 2 + O 2
2NO2 → N 2 + 2O 2
The catalyst simply separates nitrogen and oxygen from the nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen and oxygen are harmless gases while nitrous oxide is actually harmful to the environment.
Stage 2 – Oxidation
Exhaust gas without nitrogen oxide (NOx) is then passed through the catalyst The agents are platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd). The catalyst oxidizes carbonmonoxide(CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) in the exhaust gas to carbondioxide (CO 2) and water (H2O).
Reactions when oxidation takes place:
2CO + O 2 → 2CO 2
HC + O 2 → CO 2 + H 2 O (*)
Note: Reaction (*) is a general reaction. In which, HC stands for hydrocarbon. HC can be methane, ethane or other hydrocarbon.
The final gases released from the exhaust gas treatment are N2, CO 2 and H2O. Three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment units are so named because they are capable of removing the three pollutants NOx, CO and HC.
Limitations of exhaust gas treatment three-way catalyst
Limitations of 3-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment system is to use high quality fuel. If the fuel is of poor quality, fuel by-products will adhere tightly to the catalyst tube, preventing contact of the exhaust gas with the catalyst surface. This reduces the effectiveness of the catalyst. Some components can be removed at high temperatures such as sulfur, some are very difficult to remove such as lead. Sulfur is contained in both diesel and gasoline. The content of sulfur and other substances in fuel depends on fuel quality.
In Vietnam today, the highest quality fuel meets Euro II standards. For imported cars that meet emission standards up to Euro IV, the vehicle must also use fuel that meets Euro IV standards for fuel. When driving with poor quality fuel, the lifespan and functions of the exhaust filter will not operate as originally designed. Expensive three-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment units are capable of periodically removing trapped sulfur. However, this process can have side reactions, creating unpleasant-smelling gases such as H2S.
3D drawing of 3-way catalytic exhaust gas treatment system